Understanding Ultrasonic Generators and Their Importance
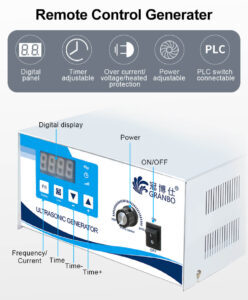
Ultrasonic generators are essential components in a wide range of applications, from industrial cleaning to medical imaging and material processing. These devices convert electrical energy into high-frequency sound waves, which then interact with various mediums to achieve desired effects. The efficiency, stability, and overall performance of ultrasonic generators rely heavily on their internal circuit design, particularly the switching integrated circuits (ICs) that regulate their operation.
Switching ICs play a critical role in power conversion, frequency control, and signal amplification within ultrasonic generators. Selecting the right ICs ensures optimal performance, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced longevity of the equipment. Understanding the functions and features of common switching ICs can help engineers and designers build more efficient and reliable ultrasonic systems.
Key Functions of Switching Integrated Circuits in Ultrasonic Generators
Switching integrated circuits are responsible for several vital functions within ultrasonic generators. Their primary roles include:

- Power Regulation: Switching ICs efficiently convert AC or DC input power to the necessary voltage and current levels required for ultrasonic wave generation.
- Frequency Modulation: Maintaining a precise frequency range is crucial for effective ultrasonic operation, and ICs enable accurate tuning and stability.
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): By modulating the pulse width of electrical signals, switching ICs control the intensity and efficiency of the ultrasonic waves.
- Overload Protection: Many modern switching ICs include built-in safety mechanisms to prevent overheating, overcurrent, and voltage spikes, enhancing the durability of the ultrasonic generator.
The ability of these ICs to switch rapidly between different states makes them ideal for managing high-frequency signals required for ultrasonic applications. As technology advances, the demand for high-performance switching ICs in ultrasonic generators continues to grow.
Common Types of Switching Integrated Circuits Used in Ultrasonic Generators

Several types of switching ICs are commonly employed in ultrasonic generators, each offering unique advantages. Some of the most frequently used ICs include:
1. MOSFET-Based Switching ICs
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) are widely used in ultrasonic generators due to their high switching speeds and efficiency. These ICs offer low power losses, making them ideal for applications where energy conservation is a priority. Common MOSFET-based switching ICs include:
- IRF540: Known for its low on-resistance and high-speed switching capabilities.
- IRLZ34N: Offers excellent performance in low-voltage applications, ensuring smooth ultrasonic signal modulation.
2. IGBT-Based Switching ICs
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) are another popular choice, especially in high-power ultrasonic applications. IGBTs combine the efficiency of MOSFETs with the high voltage and current handling capacity of bipolar transistors. Examples include:
- FGA25N120: Capable of handling high power levels while maintaining low switching losses.
- STGW30NC60W: A robust IC ideal for industrial ultrasonic cleaning applications.
3. PWM Controller ICs
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controller ICs help regulate the ultrasonic wave output, ensuring stable and efficient performance. Some well-known PWM controllers include:
- TL494: Offers excellent frequency stability and efficient pulse control.
- SG3525: Frequently used in ultrasonic power supplies due to its reliable voltage regulation capabilities.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Switching IC for an Ultrasonic Generator
When selecting a switching IC for an ultrasonic generator, several key factors should be taken into account:
- Operating Frequency: Different applications require specific frequency ranges, and the IC must support the desired frequency.
- Power Handling Capacity: The IC should match the power requirements of the ultrasonic generator to prevent overloading or inefficiency.
- Thermal Performance: Heat dissipation is a critical concern; selecting an IC with good thermal management features can prolong device lifespan.
- Efficiency: High-efficiency ICs minimize energy waste, making the ultrasonic generator more cost-effective.
- Compatibility with Other Components: Ensuring the IC works seamlessly with other circuit elements is essential for smooth operation.
By carefully evaluating these factors, designers can choose the most suitable switching IC for their specific ultrasonic applications.
Emerging Trends and Future Developments in Ultrasonic Generator ICs

As technology advances, the field of ultrasonic generators and switching ICs is continuously evolving. Some of the emerging trends include:
- Integration of AI and IoT: Smart ultrasonic systems leverage artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity to enhance precision and efficiency.
- Enhanced Miniaturization: Smaller, more compact IC designs are enabling the development of lightweight and portable ultrasonic generators.
- Higher Efficiency Power Conversion: New materials and circuit designs are improving the efficiency of power conversion in ultrasonic applications.
- Wide-Bandgap Semiconductor Materials: The use of materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) is enhancing the performance of switching ICs in high-frequency applications.
These advancements are driving the next generation of ultrasonic generators, making them more efficient, reliable, and versatile for a broad range of industries.
References
- Kazimierczuk, M. K. (2014). Pulse-Width Modulated DC-DC Power Converters. Wiley.
- Rashid, M. H. (2017). Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices, and Applications. Pearson.
- Lee, F. C., & Jovanovic, M. M. (2020). Power Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems. Cambridge University Press.
- Recent studies and industry reports from IEEE Xplore and ScienceDirect on ultrasonic power electronics and circuit design.




